What is an ERP system?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is used by organizations to manage their business processes and operations more efficiently. At its most basic, an ERP integrates all aspects of a company’s operations, including finance, accounting, human resources, purchasing and supply chain management, manufacturing, and customer relationship management, in a single, centralized system and single point of truth.
ERP projects typically forecast a 20% reduction in SG&A.
Erik Kimbering, CEO & Founder, Third Stage Consulting Group
ERP software is designed to provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s business processes, enabling managers to make informed decisions based on real-time data. They help organizations streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve productivity by automating routine tasks and providing a single source of truth for all business data.
Material requirements planning (MRP) and manufacturing resource planning (MRPII) software are the grandparent’s of today’s ERP software. Over the years, the scope of ERP software has grown to encompass a wide range of business-related functions. A key benefit of ERP software is that it can help organizations improve their decision-making capabilities by providing real-time data and analytics. This can help managers identify trends, track performance, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic planning, enabling a business to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and improve productivity.
ERP software is typically organized in modules, each module focuses on a specific aspect of the business. For example, the General Ledger module might provide the fundamentals for basic double entry accounting, including a chart of accounts, balance sheet and income statement, a Inventory module might provide the essential concepts to describe a product, various characteristics and how the quantity of a product is measured, and the Purchasing module might include everything required to create and manage purchases made by the company. Modularity reduces complication for the user and modules not required by the business can be hidden from users.
Common ERP Functions
Common functions of an ERP system include:
- Selling products and services to customers
- Purchasing products and services from suppliers
- Accounting and financial reporting
- Managing staff
- Fixed assets management
- Managing manufacturing
- Managing prospective customers
Let us briefly drill down into each of these functions.
Selling products and services to customers
A sales order is generated when a business is selling something to a customer, and may be the response when a customer purchase order is received. A sales order may start as a quote and progress to a sales order once the prospective customer has decided to purchase.
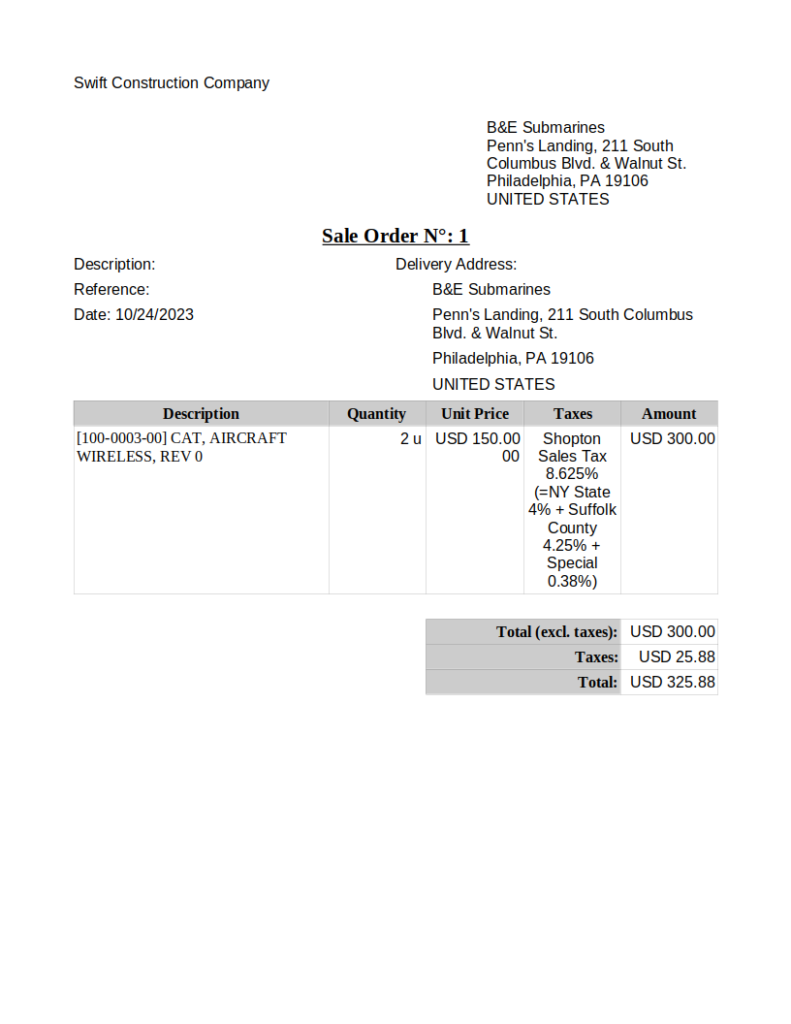
Often the product is shipped to the customer (or services have been provided) before the customer is invoiced. However, a customer customers must have to pay in advance before product is shipped, and sometimes a customer must make a deposit before product is even manufacture. The rules vary from company to company, customer to customer, and product to product.
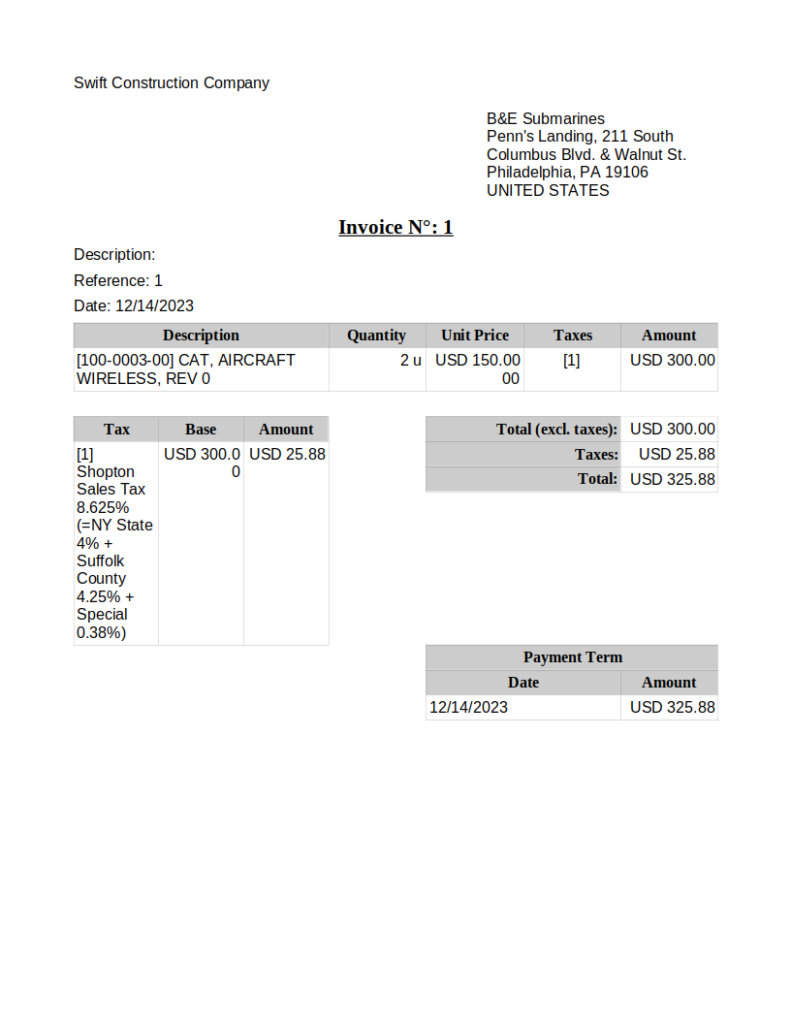
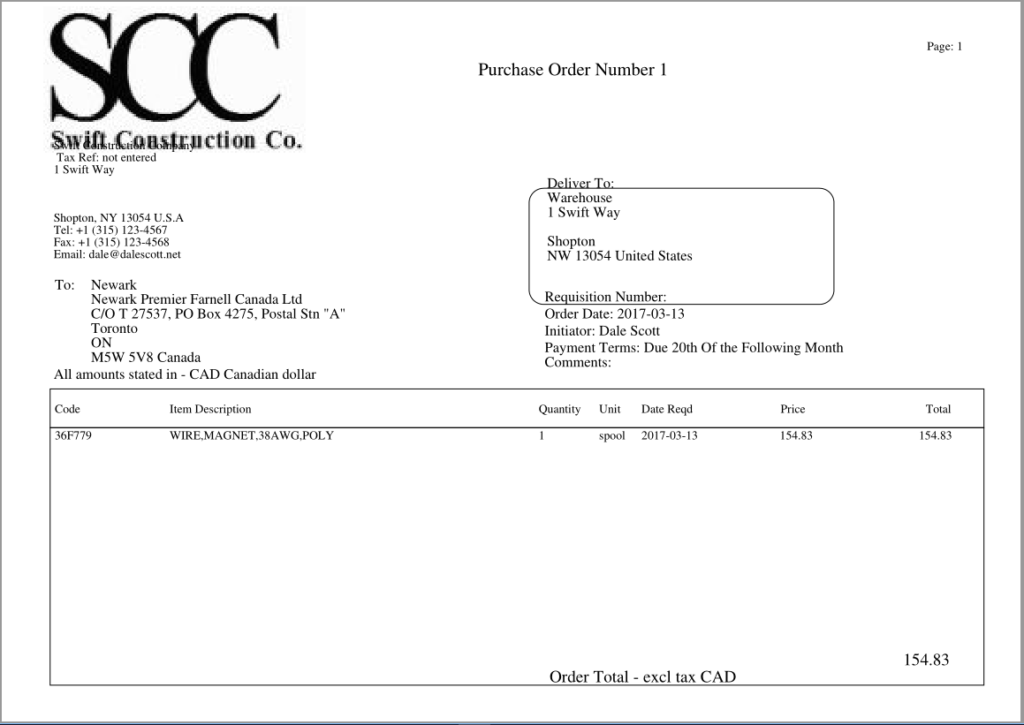
Purchasing products and services from suppliers
A Purchase Order (PO) is generated when a company wishes to purchase product or services from a vendor (or supplier). An ERP typically includes features to manage vendors as well as the products they sell. Often purchase orders are created in draft form, before being approved and issued to a customer.
Often a sales orders and purchase orders are linked in a process to streamline business operations. A sales order creates demand in an ERP system for the product being purchased, and if there is no stock of the product on hand (and if the ERP system is configured appropiately) either a purchase order or manufacturing order can be automatically generated to replentish stock. When used properly, an ERP can increase purchasing efficiency and assist in avoiding stock shortages.
Accounting and financial reporting
A major role of an ERP system is bookkeeping and the generation of financial statements and various reports indicating the state of the business. The accounting functionality centers on structures known as the General Ledger (GL) and Chart of Accounts. The chart of accounts organizes groups of transactions into categories such as assets, liabilities, income, and expenses, to meet the specific requirements of a business.
Accounting transactions are grouped into periods by date (typically months, quarters and years) for reporting on. The reports are called financial statements, which usually include a balance sheet, an income statement, a cash flow statement, and statement of owner’s equity.
Managing staff
An ERP may include features to manage staff, often called Human Resource (HR). Specific features commonly provided include attendance and leaves, time allocation, benefits and compensation administration, payroll, recruiting, competency tracking and training.
Managing fixed assets
Fixed asset management involves tracking and maintaining an organization’s physical assets, which includes equipment, vehicles, furniture, and machinery. Organizations can report on fixed assets more efficiently for financial reporting, and track and monitor assets for effective management to lower maintenance costs, reduce equipment downtime, and improve operational efficiency.
Managing manufacturing
Manufacturing can be a complicated process, which an ERP can aid by manages the various business operations involved. The fundamental transaction in the manufacturing process is a manufacturing order (also called a production order). A manufacturing order describes the inputs to the manufacturing process (the raw materials consumed in the manufacturing process), the outputs of the process (also called finished goods), and the steps to get from input to output, called routings and work centers.
A product is typically described in a hierarchical list of sub-assemblies and raw material called a Bill of Materials (BOM). A BOM also lists the exact quantities of materials needed, using the appropriate unit of measure (UOM) for each material (such as units, meters, kilograms, or litres). If a business manufactures several products, there are often common raw materials, which must be taken into account when planning manufacturing.
Often a business will have multiple locations or warehouses where raw materials and finished goods are stored, and an ERP system will include features to manage stock in multiple locations, including work-in-process (WIP).
Managing customers
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a popular term for a system to identify prospective customers (typically called leads or opportunities), and manage their journey to customer in a structured and reportable process. CRM also often includes managing marketing campaigns.
CRM features are typically used most by the sales and marketing departments within a company, and are also called sales force automation tools. CRM can include creating and managing apointments, scheduling follow-up, and communication management including social networking channels.
